Global Water Scenario
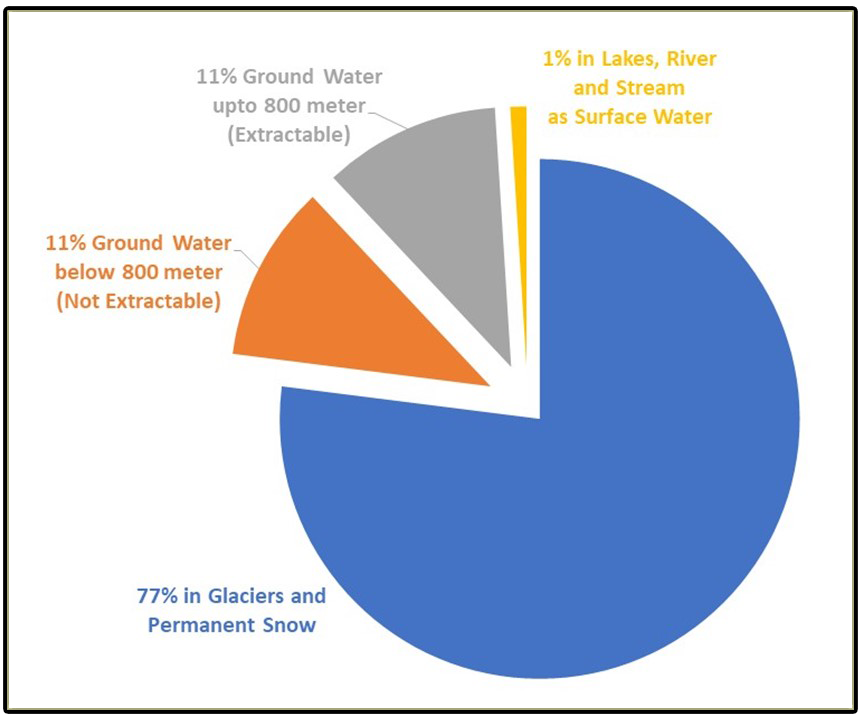
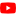
Water is one of the basic necessities of every living being for their survival. Many of us have an image of the world as a blue planet as 70 percent of the earth’s surface is covered with water. The reality, however, is that 97 % of the total water on earth is saline and only 3 % is available as freshwater. About 77 % of this freshwater is locked up in glaciers and permanent snow and 11 % is considered to occur at depths exceeding 800 meters below the ground, which cannot be extracted economically with the technology available today. About 11 % of the resources are available as extractable groundwater within the 800 meters depth and about 1 % is available as surface water in lakes and rivers. Currently 69% of all water withdrawn for human use on an annual basis is soaked up by agriculture, industry accounts for 23% and domestic use (household, drinking water, sanitation) accounts for about 8%.
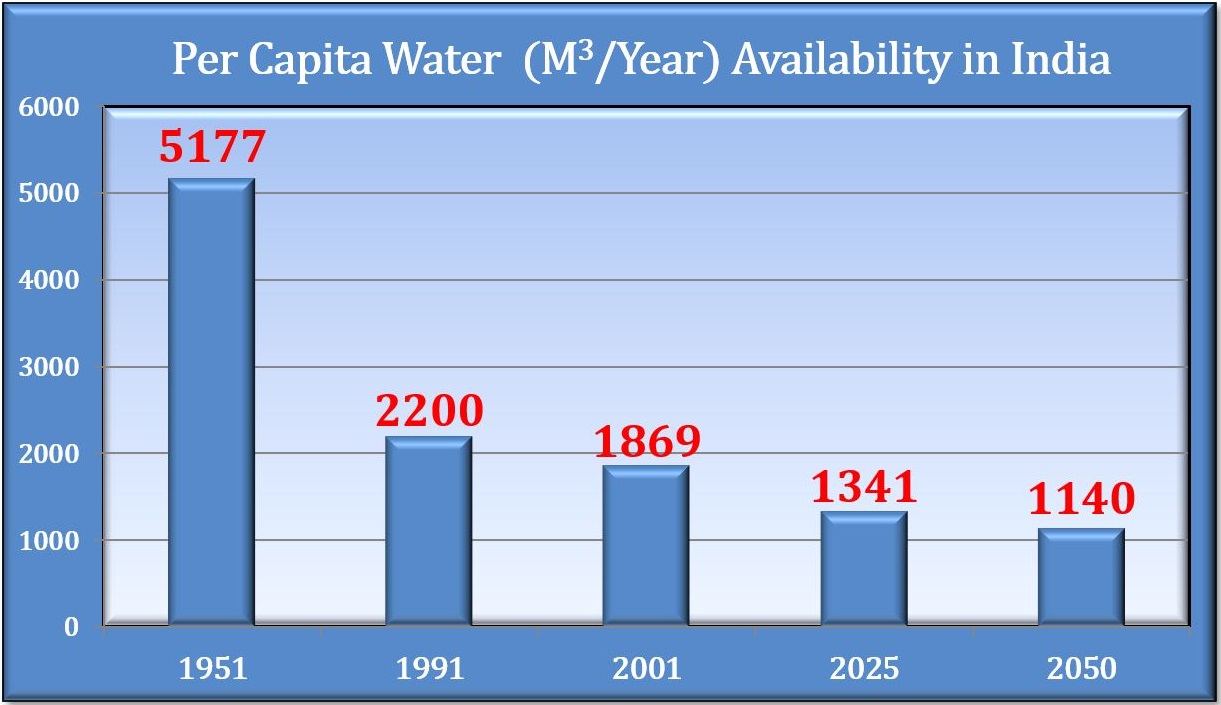
The total water resources available for various uses, on an annual basis, are of the order of 1123 BCM. Although the per capita availability of water in India is about 1869 m3 as in 1997 against the benchmark value of 1000 Cu m signifying ‘water-starved’ condition, there is a wide disparity in basin- wise water availability due to uneven rainfall and varying population density in the country. The availability is as high as 14057 m3 per capita in Brahmaputra/Barak Basin and as low as 307 m3 in the Sabarmati basin. Many other basins like Mahi, Tapi, Pennar are already water-stressed.
| BENCH MARKS | |
|---|---|
| Water Stress | Between 1700 and 1000 M3 /Year Person |
| Water Scarcity | Below 1000 M3/Year/Person |
Indian Water / Rainfall Scenario
In India, it is estimated that sectoral water requirements by 2010 are 85%, 7%, 5% and 3% foragriculture, domestic, industries and energy, respectively.The geographical area of India is about 329 million hectares (2.45 % of the earth’s land mass) and population is 1.324 billion in 2016, which is 16% in the world. India receives 400 million-hectare meters (mham) of rain and snowfall. Another 20 mham flow in as surface water from outside the country. This total 420 mham provide the country with river flows of 180 mham. Another 67 mham is available as groundwater. About 173 mham is lost as evaporation or becomes soil moisture - which can be captured directly as rainwater or as runoff from small catchments in and near villages or towns. If even 20 mham can be captured through rainwater harvesting, tremendous pressure can greatly extend the availability of clean water.
Facts about Water in Surat
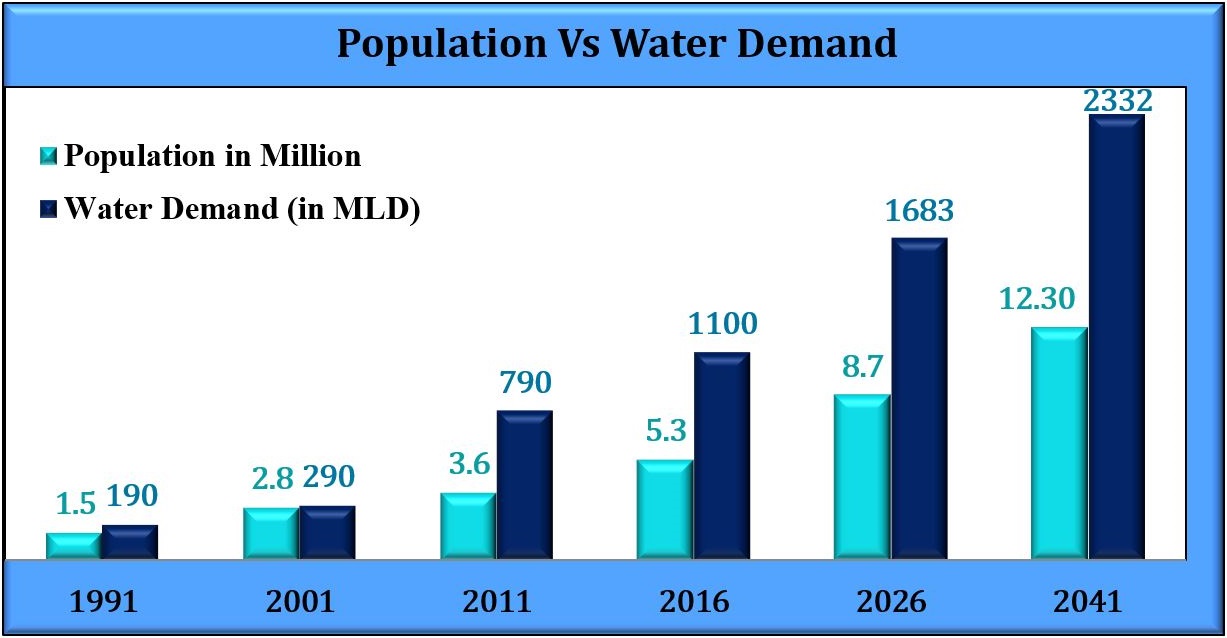
Surat is 2nd largest city of Gujarat in the terms of 326.515 Sq. Km area and 8th largest city in India in the terms of 4.5 Million population at the 2011 enumeration, making it the second-largest city in Gujarat after Ahmadabad. It has been seen that every year the population increased by 4.5 % average. Hence, the population of Surat in 2021 is forecasted to be 6.9 million. Surat is situated at the tail end of the 750 km long River Tapi which has been the main source of water for the city for centuries. With the increasing population of the city, water demand has been increased accordingly.
What is Groundwater Recharging?
Groundwater is recharged naturally by rain and to a smaller extent by surface water (rivers and lakes). Recharge may be impeded somewhat by human activities including paving, development, or logging. These activities can result in loss of topsoil resulting in reduced water infiltration, enhanced surface runoff and reduction in recharge. Use of groundwaters, especially for irrigation, may also lower the water tables. Groundwater recharge is an important process for sustainable groundwater management, since the volume-rate abstracted from an aquifer in the long term should be less than or equal to the volume-rate that is recharged. Recharge can help move excess salts that accumulate in the root zone, or into the groundwater system. Read More
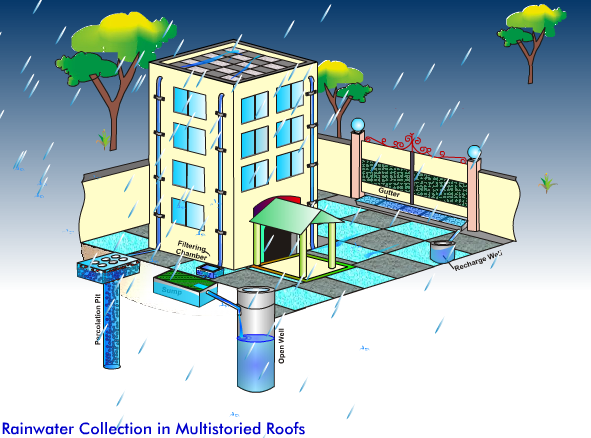
Advantages of Rainwater Harvesting/Groundwater Recharging
- It improves the quality of existing ground water and helps to replenish it.
- It will help in reducing the flood hazards.
- It also reduces soil erosion in urban areas.
- Ideal solution in areas where there is inadequate groundwater supply or surface resources are either lacking or insufficient.
- It reduces the cost for pumping of ground water.
- It helps in utilizing the primary source of water and prevents the runoff from going into sewer or storm drains, thereby reducing the unnecessary load on treatment plants.